
What is an Atomizing Nozzle?
Atomizing nozzles are specialized nozzles that disperse liquid, or sometimes gas, by breaking it up into fine droplets (atoms). The term "atomization" refers to the process of breaking a liquid into very small droplets. Atomizing nozzles typically convert liquid into fine particles using gaseous (air) atomization, mechanical atomization, or steam atomization methods.
The biggest advantage of these nozzles is the homogeneous distribution of liquids. Atomizing nozzles are used in a wide range of applications, including industrial cooling, humidification, paint spraying, liquid spraying, and even the efficient evaporation of liquids in some medical applications.
Types of Atomizing Nozzles
Atomizing nozzles can be divided into different types according to their working principles. The most common atomization techniques are:
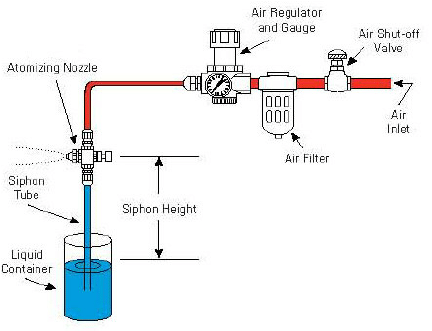
Air Atomization (Air Atomizing Nozzle)
Working Principle: These nozzles allow liquid to be broken into fine droplets by combining liquid and air flow. While the air flow atomizes the liquid, the droplet sizes decrease as the air pressure increases towards the outlet.
Applications: Painting, spray drying, cooling, humidification.
Mechanical Atomization (Mechanical Atomizing Nozzle)
Working Principle: These types of nozzles atomize the liquid by passing it through a rapidly rotating part. They usually contain disc or button-shaped tips.
Applications: Industrial cooling, spray drying, chemical processes.
Steam Atomization (Steam Atomizing Nozzle)
Working Principle: Steam is used to atomize the liquid. These nozzles typically allow the steam to atomize the liquid by hitting it at high speed.
Applications: Chemical processes, heating, food processing.
Liquid Atomization (Liquid Atomizing Nozzle)
Working Principle: These nozzles use only liquid flow to break the liquid into fine droplets and usually operate under high pressure.
Applications: Washing, cooling, humidification.
Technical Data and Numerical Information of Atomizing Nozzles
| Feature | Values |
| Nozzle Type |
Air Atomization, Mechanical Atomization, Steam Atomization
|
| Connection Type |
Threaded, flanged connection options
|
| Flow Rate Range |
0.1 L/min - 1000 L/min (varies depending on nozzle type)
|
| Operating Pressure |
2 bar - 50 bar (varies depending on pressure)
|
| Droplet Size |
5 - 100 microns (varies depending on pressure and air flow)
|
| Outlet Angle |
30° - 120° (spread angle)
|
| Outlet Type |
Fine spray, fan-shaped, conical spray
|
| Temperature Range |
-10°C to 250°C (depending on material type)
|
| Material Selection |
Stainless steel (SS304, SS316), aluminum, copper, PTFE, PVC
|
| Application Areas |
Cooling, humidification, spray drying, painting, industrial cleaning
|
| Nozzle Sizes |
Ø0.5mm - Ø8mm (diameters are usually selected according to flow rate requirements)
|
| Surface Coverage Area |
0.1 m² - 50 m² (varies depending on flow rate and outlet angle)
|
Usage Areas of Atomizing Nozzles
Painting and Coating Applications:
Atomizing nozzles are widely used in paint spraying processes. Fine droplets provide a more even and homogeneous coating on the surface. This is a common use in the automotive, textile, construction, and electronics industries.
Cooling and Humidification:
In industrial cooling systems, atomizing nozzles are used to reduce the temperature of machines or systems. They are also effective in humidifier systems, especially in air humidification and greenhouse applications.
Spray Drying:
The spray drying process involves atomizing liquids and evaporating them by rapidly drying them. This technology is used in the food processing, chemical, and pharmaceutical industries.
Liquid Spraying and Chemical Processes:
In the chemical industries, atomizing nozzles are used for many applications where liquids need to be evenly distributed. These nozzles help accelerate chemical reactions by converting liquids into microscopic droplets.
Fire Extinguishing:
Atomizing nozzles are also used in fire extinguishing systems. Thanks to fine droplets, fire extinguishing agents can be spread over a wider area and effectively extinguish the fire.
Food Processing:
In the food industry, atomizing nozzles are used in some processes where liquids need to be atomized into fine droplets. For example, oil spraying, adding sweeteners, or water evaporation processes on food.
Advantages of Atomizing Nozzles
Homogeneous Distribution: Atomizing nozzles spread liquids homogeneously, ensuring that each area is covered with the same amount of liquid.
Energy Efficiency: Thanks to fine droplets, liquids evaporate or disperse faster, which increases energy efficiency.
High Efficiency: Through atomization, liquids are spread more effectively to target areas, so larger areas can be covered with less liquid.
Quick Installation and Maintenance: Especially in industrial applications, the installation and maintenance of atomizing nozzles are usually easy.
Conclusion
Atomizing nozzles are important tools that increase efficiency and save energy by allowing liquids to be atomized homogeneously in industrial applications. Various types can be used in many sectors with different flow rates and pressure ranges. In areas such as painting, cooling, humidification, chemical processes, and food processing, atomizing nozzles offer effective and fast solutions.











