
Nozzle Spray
Spray nozzles are industrial tools used to atomize liquids or gases in a specific way and evenly. These nozzles are used in a wide range of industrial applications, from cleaning to cooling systems. Especially in cases where liquids need to be atomized in micro sizes, nozzle spray systems increase efficiency and effectiveness. In this article, detailed information with numerical data about the technical specifications, usage areas, and application examples of spray nozzles will be given.
Basic Working Principle of
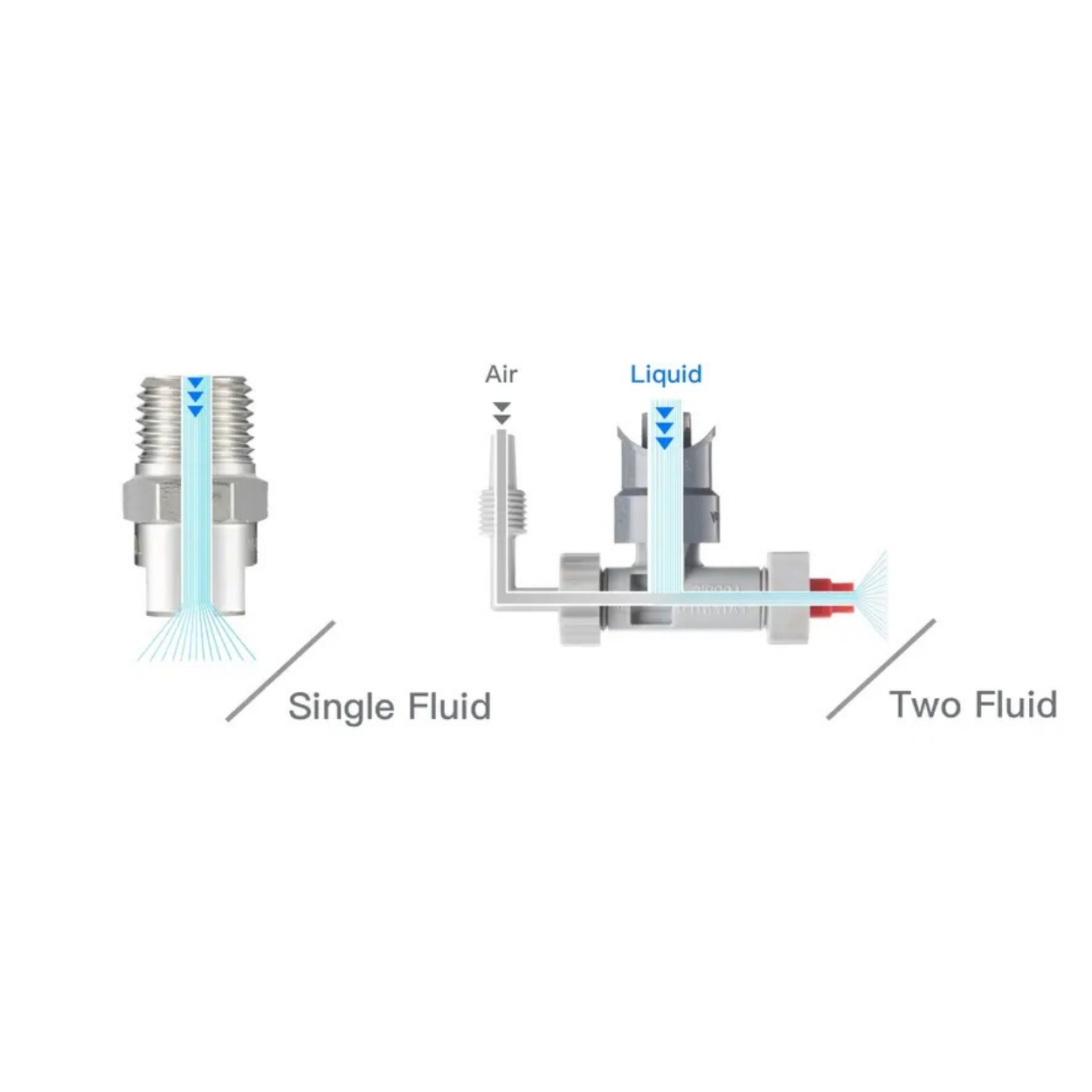
Spray nozzles separate liquids or gases into fine particles under high pressure and bring them into contact with the atmosphere. This atomization process allows the liquid to spread evenly over the surface. The spraying process usually varies depending on factors such as pressure, flow rate, and nozzle design.
Spray nozzles are used in various fields and may have different technical specifications for each application. The spray pattern provided by a good spray nozzle provides a mist consisting of very small and homogeneous droplet sizes.
Technical Specifications and Numerical Data of Spray Nozzles
Connection Type and Dimensions:
Connection Type: Usually female threaded connections such as 1/8 inch, 1/4 inch, 1/2 inch, 3/4 inch are used.
Connection Location: Connection locations are located at the inlet and outlet heads and are usually made of stainless steel or aluminum material.
Spraying Type:
Full Cone: Liquid is sprayed in wide areas at angle ranges varying between 60° - 120°.
Flat Fan: It usually has an angle between 30° - 110° and provides liquid distribution over a wide and flat area.
Round Atomizer: Produces small, dense sprays with angles varying between 0° - 15°.
Spraying Angles and Area:
Outlet Angles: Nozzles usually have an outlet angle between 30° - 120°.
Spraying Area: This area, which varies depending on the outlet angle and flow rate, can expand from 1 square meter to 100 square meters.
Flow Rate and Pressure:
Flow Rate: The flow rate of spray nozzles can vary between 1 L/min and 500 L/min depending on the material used and the design of the nozzles.
Pressure: Commonly used pressure ranges vary between 1 bar – 15 bar. As the pressure increases, the atomized droplet sizes become smaller.
For example, while large droplets are sprayed at 2 bar pressure, finely atomized droplets are sprayed at 10 bar pressure.
Droplet Size:
Droplet Size: The atomization power of these nozzles can atomize liquid at droplet sizes between 50 microns and 300 microns.
Ideal Droplet Size: Usually, droplet sizes are around 50 microns for ideal atomization. These sizes ensure that the liquid spreads efficiently and is evenly distributed on the target surface.
Material:
Stainless Steel: It is usually preferred for nozzles that are corrosion resistant, high temperature and pressure resistant.
Plastic (PVC, PP): Used in applications requiring chemical resistance.
Bronze and Aluminum: Used as durable and economical alternatives.
Ceramic: It is preferred in applications resistant to abrasive chemicals and high temperatures.
Usage Areas of Spray Nozzles
Industrial Cleaning:
Application: High-pressure spray nozzles are used to clean dirt and residues on machines and production lines.
Numerical Data: The flow rate of most industrial cleaning nozzles is between 10 L/min and 100 L/min and operates at a pressure between 3 bar and 8 bar.
Agriculture and Irrigation:
Application: It is used in the agricultural sector for the proper spreading of pesticides and fertilizers. It is also widely used in irrigation systems to distribute water evenly.
Numerical Data: The flow rate of a typical irrigation nozzle varies between 20 L/min and 200 L/min. The spray angle can usually be between 90° - 120°.
Cooling Systems:
Application: Nozzles used in industrial cooling systems allow liquids to mix with air and cool hot surfaces.
Numerical Data: They usually operate at a pressure of 5 bar – 10 bar and have flow rates varying between 1 L/min and 50 L/min.
Misting and Evaporation:
Application: It is used in agriculture, in greenhouses or large areas to control the humidity level and to distribute particles in the atmosphere.
Numerical Data: The droplet size is usually between 20 microns – 50 microns and they can operate at flow rates varying between 0.5 L/min and 30 L/min.
Food Industry:
Application: In food processing facilities, it is used for disinfection and cleaning, especially during fruit and vegetable washing, meat processing and freezing.
Numerical Data: Nozzles used for washing processes usually operate at a pressure of 5 bar to 8 bar and can have a flow rate of 10 L/min to 40 L/min.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Spray Nozzles
Advantages:
High Efficiency: By atomizing the liquid into small droplets, it ensures that more liquid reaches the target surface.
Fast Application: It enables large areas to be cleaned, cooled or irrigated quickly.
Low Energy Consumption: Thanks to efficient liquid atomization, energy consumption is kept to a minimum.
Various Application Areas: It has a wide range of uses such as industrial, agriculture, automotive, food processing.
Disadvantages:
Equipment Cost: High-quality and specially designed nozzles can be costly initially.
Difficulty of Use with Abrasive Liquids: When used with abrasive substances, the materials of the nozzles can wear out quickly.
Conclusion:
Spray nozzles offer a versatile, efficient and effective solution in liquid distribution. Their high capacities, small droplet sizes and wide spray angles enable the nozzles to be used in a wide variety of industrial applications. These systems, which can be customized based on factors such as flow rate, pressure and droplet size, offer suitable options for all kinds of industrial and agricultural needs. Nozzle design is of critical importance in terms of efficiency and durability, so making the right choice will increase application efficiency.











