
Venturi Mixing Eductor
Venturi mixing eductors are incredibly versatile tools used in a wide range of industries. Their unique design and operational principles make them ideal for specific applications. Here are some key scenarios where you would consider using a venturi mixing eductor:
Handling Corrosive or Abrasive Fluids:
Chemical Processing: Mixing strong acids, bases, or other corrosive chemicals.
Wastewater Treatment: Handling sludge, slurries, and other abrasive materials.
Self-Priming Applications:
Lifting Fluids from Lower Levels: Ideal for applications where the fluid needs to be lifted from a lower level, such as sump pumps or transfer pumps.
Mixing Incompatible Fluids:
Emulsification: Creating emulsions of oil and water.
Dispersion: Dispersing solids in liquids.
Vacuum Creation:
Vacuum Systems: Generating a vacuum for various processes, such as filtration or evaporation.
Gas-Liquid Mixing:
Aeration: Aerating liquids for biological processes.
No Moving Parts Required:
Sterile Environments: Where contamination from moving parts is a concern.
Hazardous Areas: In environments where sparks or heat can ignite flammable materials.
Specific Applications:
Food Processing: Mixing ingredients and cleaning equipment.
Oil and Gas Industry: Mixing drilling fluids and other fluids.
Pharmaceutical Industry: Mixing pharmaceutical compounds.
Advantages of Venturi Mixing Eductors:
No moving parts: Reduces maintenance and increases reliability.
Self-priming: Can lift fluids from lower levels.
Handles a wide range of fluids: From gases to slurries.
Compact and efficient: Requires minimal space.
In summary, venturi mixing eductors are excellent choices when:
You need to handle corrosive or abrasive fluids.
Self-priming is a requirement.
You want to mix incompatible fluids.
A vacuum is needed.
Moving parts are undesirable.
Venturi Eductor: A Comprehensive Guide
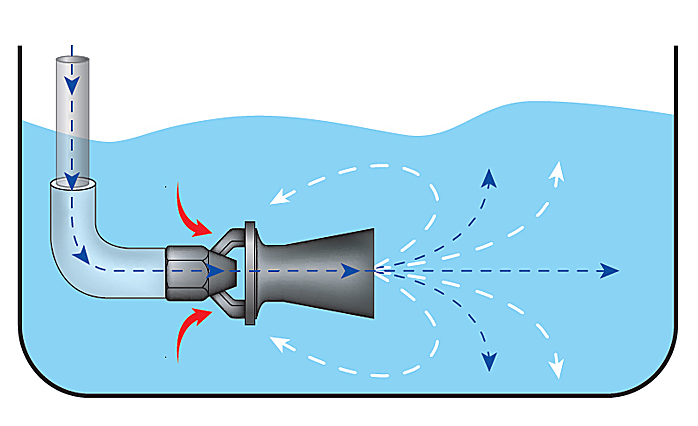
1. Working Principle and General Structure
A Venturi eductor leverages the Venturi effect to mix fluids. This principle states that as a fluid passes through a constricted section (nozzle), its velocity increases while its pressure decreases. The resulting pressure drop creates a vacuum, which draws in another fluid or gas for mixing.
Components:
Inlet Nozzle: The point where the fluid enters at high velocity.
Mixing Zone (Venturi Region): The section where the fluid accelerates and the vacuum effect induces mixing.
Outlet Nozzle: The point where the mixed fluid exits.
2. Technical Specifications and Performance
The following data represents typical performance characteristics of a Venturi eductor used in industrial applications:
| Feature | Value |
| Operating Temperature |
-10°C to 150°C (varies based on material)
|
| Operating Pressure |
2 bar to 10 bar (maximum operating pressure)
|
| Flow Rate Range |
0.5 m³/h to 5000 m³/h
|
| Efficiency |
Over 90% (mixing efficiency)
|
| Liquid/Gas Mixture Ratio |
1:1 to 1:10 (ratio of liquid to gas in the mixture)
|
| Nozzle Diameter |
20 mm to 200 mm (varies based on model and flow rate)
|
| Material Selection |
Stainless steel, cast iron, PVC, PVDF, Hastelloy, etc.
|
| Outlet Velocity |
5 m/s to 30 m/s (higher velocities possible depending on application)
|
| Vacuum Pressure |
0.1 bar to 0.9 bar (for mixing)
|
| Eductor Type |
Vertical or horizontal configurations available
|
| Applications |
Chemical industry, water treatment, food and beverage, oil and gas sectors
|
3. Sizing and Capacity Calculation
Proper sizing of a Venturi eductor is crucial for achieving the desired mixture ratio and flow rate. Below are some basic calculations involved in sizing.
Flow Rate Calculations:
Inlet Fluid Flow Rate (Q_in): Q_in = A_in × V_in Where:
A_in = Inlet cross-sectional area (m²)
V_in = Inlet fluid velocity (m/s)
Outlet Fluid Flow Rate (Q_out): Q_out = Q_in × Efficiency For 90% efficiency: Q_out ≈ Q_in × 0.9
Mixture Ratio: Typically, a Venturi eductor can entrain approximately 10 times the volume of gas compared to the liquid (1:10 ratio). However, this ratio can vary depending on the substances being mixed and the eductor's design.
4. Application Areas and Example Calculations
Water Treatment: Venturi eductors are commonly used for chemical dosing, pH adjustment, and flocculation in water treatment plants.
Chemical Industry: Venturi eductors are ideal for mixing chemicals, such as neutralizing an acid with a base.
5. Summary
Venturi eductors find wide application in various industries for mixing, dosing, and liquid-gas transfer. These devices offer high efficiency and low energy consumption. Technical details and sizing can be customized to meet specific application requirements.
Please note:
Unit Conversions: 1 m³/h = 3.531 ft³/h, 1 bar ≈ 14.5 psi.
For more specific calculations and applications, consult engineering references and manufacturers' guidelines.
eductor , veturi mixing eductor, nozzle











