
Flat Jet Nozzle
Flat Jet (Flat Fan) Nozzles – Working Principles and Applications
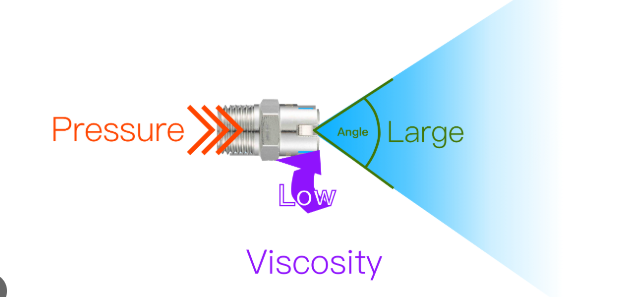
What Is a Flat Jet Nozzle?
Flat jet nozzles produce a strip‑shaped spray pattern rather than a round cone. A typical flat jet nozzle uses a fluid under pressure, forces it through a carefully shaped outlet and then allows it to expand into a thin sheet. The nozzle distributes more liquid in the centre of the spray than at the edges; engineers therefore space multiple nozzles so their spray patterns overlap to achieve uniform coveragehttps://spreynozul.org/urun/flat-jet-sprey-nozul.html
Working Principles
Flat jet nozzles use one of two basic methods to create the fan‑shaped spray:
-
Shaped (elliptical) orifice design. The simplest design uses an elliptical or slotted orifice. The fluid exits the shaped opening and immediately forms a flat sheet https://spreynozul.org/urun/flat-jet-sprey-nozul.htmlBecause the orifice itself shapes the spray, this design is sometimes called a “pressure” or “shaped‑orifice” nozzle. The edges of the spray taper off, so engineers install several nozzles in a row with slight overlaps to achieve even coveragespreynozul.org
-
Deflector design. In a deflector (or deflection) nozzle, the fluid first passes through a circular orifice and then strikes a curved or sloping surface. The impact both atomises the liquid and redirects it sideways, spreading it into a flat fan pattern https://spreynozul.org/urun/flat-jet-sprey-nozul.htmlBecause the orifice can remain round and relatively large, deflector nozzles resist clogging and wearhttps://spreynozul.org/urun/flat-jet-sprey-nozul.html High‑impact variants trade spray angle for a harder, more focused spray.
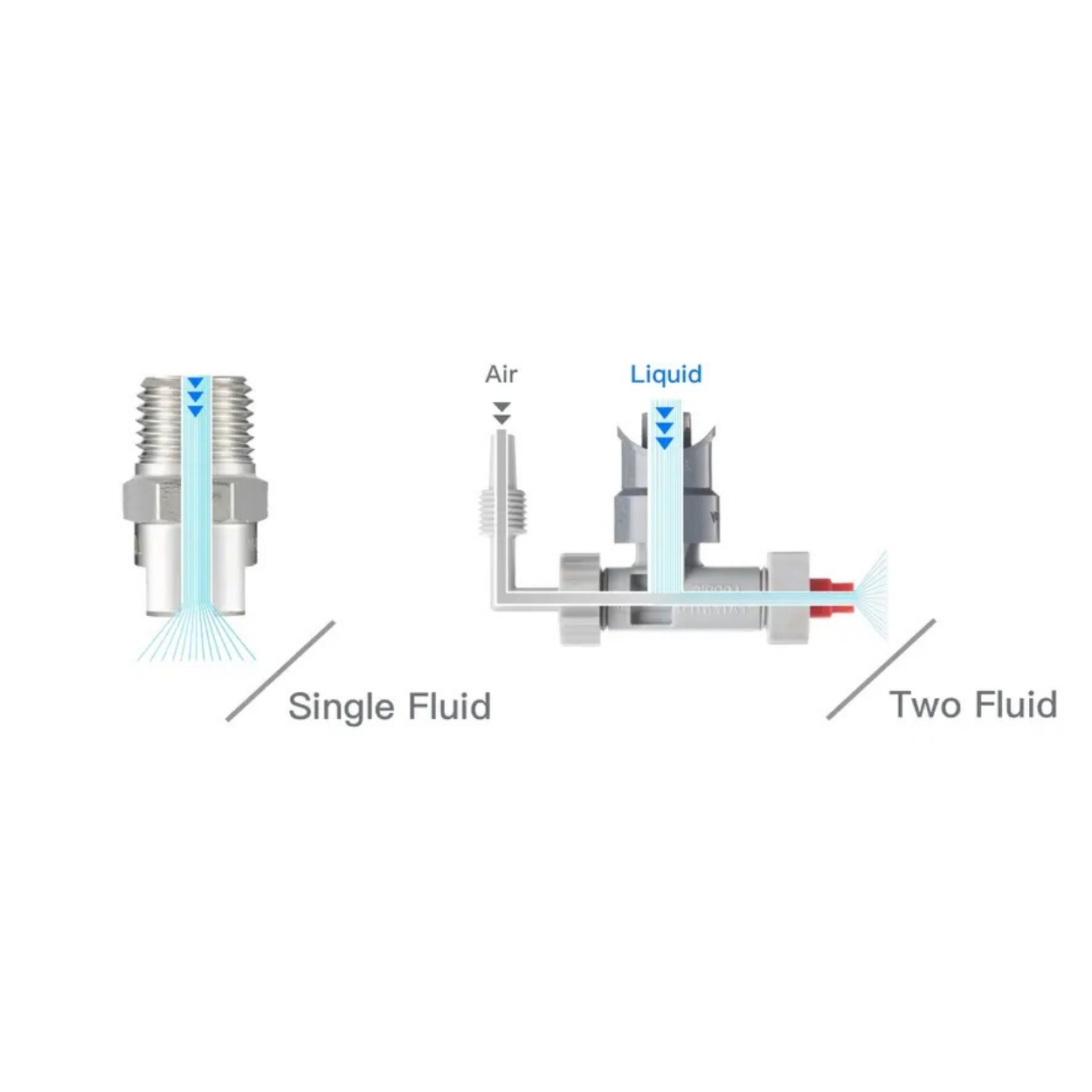
A technical note summarises these two approaches: flat‑fan sprays can be created either by a simple shaped orifice or by deflecting a jet on a shaped surfacespray-nozzle.co.uk. The deflection approach is exemplified by the “K‑series” nozzles, which direct the jet onto a sloping surface to change its flow direction and produce a fan‑shaped misthttps://spreynozul.org/urun/atomizing-hava-su-nozulu.html
Spray Angle, Pressure and Droplets
Standard flat‑fan nozzles operate between about 30–60 psi, with the ideal range around 30–40 psi for agricultural applications Deflector and special‑feature designs may work at lower pressures or produce higher‑impact sprays. Common spray angles are 65°, 80° and 110°https://spreynozul.org/urun/flat-jet-sprey-nozul.html. Narrower angles produce a more concentrated jet and larger droplets, while wider angles give broader coverage with smaller droplets. Regardless of the design, the thin sheet of liquid quickly breaks into droplets due to air drag and surface tension.
Applications
Flat jet nozzles are versatile and are used wherever a band‑shaped spray is beneficial:
-
Cleaning and surface preparation: High‑impact flat jets are widely used in pressure washing, steel descaling and conveyor belt cleaning.
-
Coating and lubricating: Elliptical‑orifice nozzles provide uniform coverage for applying lubricants, coatings, paints or adhesives.
-
Agricultural spraying: Flat‑fan nozzles are common on boom sprayers for herbicides, pesticides and fertilisers; standard, even and extended‑range designs allow operators to balance droplet size, drift control and coverage
-
Cooling and humidification: Flat jets cool moving webs, strips or rolls in metal processing, and they humidify surfaces in paper and textile manufacturing.
Key Takeaways
A flat jet nozzle forces pressurised liquid into a thin sheet that spreads out like a fan. Two distinct mechanisms create this spray: a shaped (elliptical) orifice that directly forms the sheet www.mitsuda.com.tr and a deflection surface that redirects a circular jet into a flat pattern spreynozul.org Understanding these working principles helps in selecting the right flat jet nozzle for applications ranging from gentle misting to high‑impact cleaning.



